As we move deeper into the digital age, branding is evolving faster than ever. Businesses must stay ahead of the curve to remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic marketplace. The year 2025 brings fresh challenges and opportunities, requiring brands to rethink their strategies and embrace innovation. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the top branding trends that will define the future and help businesses create a powerful, lasting impact.
Hyper-Personalization with AI: The age of tailored experiences
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing branding by enabling hyper-personalized experiences. Companies now use AI-powered data analytics to track customer behavior, predict preferences, and create customized content. This extends to personalized product recommendations, automated email marketing, chatbots that provide real-time customer support, and even dynamic pricing strategies.
Brands that leverage AI-driven personalization will stand out by delivering meaningful and relevant experiences tailored to individual consumers. As machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, businesses that fail to integrate AI into their marketing strategies risk being left behind in an era where customers expect tailor-made interactions.

Decentralized branding and community engagement: Power to the people
Decentralization is redefining brand ownership, shifting power from corporations to consumers. With the rise of Web3 and blockchain technology, customers are no longer just passive buyers; they are active participants in shaping brand identity.
- Community-Driven Branding: Companies are encouraging customer co-creation by allowing users to contribute ideas, vote on product designs, or even own digital assets (NFTs) that give them special privileges.
- Blockchain-Based Transparency: Consumers demand greater transparency, and blockchain provides an immutable record of a company’s supply chain, ethical sourcing, and product authenticity.
- Loyalty Programs Reinvented: Traditional loyalty programs are evolving into decentralized reward systems where customers earn tokens or digital assets that hold real-world value.
Brands that embrace this shift by prioritizing community engagement, transparency, and decentralized decision-making will foster deeper customer loyalty and trust.

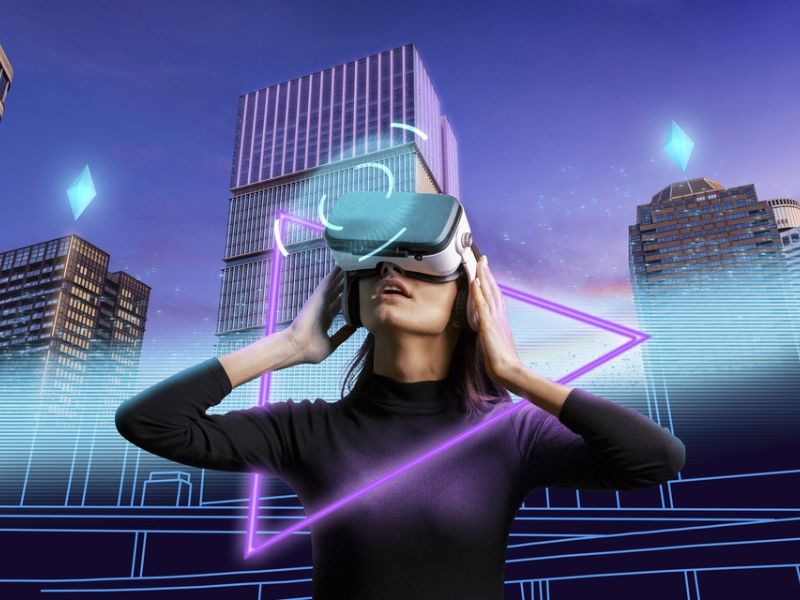
Immersive experiences with AR and VR: The future of brand interaction
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are transforming how consumers interact with brands. These technologies provide immersive storytelling opportunities that captivate audiences and drive engagement.
- Virtual Showrooms & Try-Ons: Retail brands are using AR-powered try-ons for fashion and makeup, while automotive companies allow customers to explore vehicles virtually.
- Interactive Advertising: AR-enabled advertisements provide interactive, 3D experiences that make digital ads more engaging and memorable.
- Branded Metaverse Experiences: Companies are establishing virtual spaces where users can explore branded environments, attend virtual events, and even make purchases in digital marketplaces.
By integrating AR/VR into their marketing strategies, brands can offer more engaging and interactive experiences that foster deeper connections with their audiences.

Sustainability and ethical branding: A non-negotiable imperative
Consumers are becoming more conscious of sustainability and ethical business practices. Brands that demonstrate genuine commitment to eco-friendly initiatives, ethical sourcing, and social responsibility will gain customer trust and loyalty.
- Eco-Conscious Packaging: Businesses are switching to biodegradable, reusable, or minimalistic packaging to reduce waste.
- Carbon Neutral Operations: Companies are pledging to achieve carbon neutrality by reducing emissions, investing in renewable energy, and adopting greener supply chain solutions.
- Social Responsibility & Inclusion: Modern consumers expect brands to take a stand on social issues, from diversity and inclusion to fair labor practices and charitable contributions.
Transparency and accountability are no longer optional. Brands that practice what they preach and communicate their efforts effectively will stand out in a competitive marketplace.

AI-Generated content and automation: The new age of digital marketing
AI-powered tools are streamlining content creation, from automated copywriting to AI-generated visuals. This trend allows brands to scale their content marketing efforts while maintaining consistency and creativity.
- AI-Generated Blogs & Ads: AI can analyze search trends and customer preferences to create SEO-optimized blogs, social media posts, and ad copy.
- Automated Video Production: AI tools can generate short-form videos based on text prompts, making video marketing more accessible to brands of all sizes.
- AI-Powered Design: Generative AI is being used to create logos, graphics, and even brand identity elements in a matter of seconds.
While AI-driven automation enhances efficiency, human oversight remains crucial to ensure authenticity and emotional resonance in brand storytelling.

Voice search optimization: The rise of conversational branding
With the growing popularity of smart speakers and voice assistants, optimizing for voice search is becoming essential for brands. Traditional SEO strategies must adapt to conversational queries and natural language searches.
- Conversational Content: Brands must optimize content for question-based queries, such as “What is the best organic coffee brand near me?”
- Local SEO for Voice Searches: Since many voice searches have local intent, businesses must ensure their location-based information is accurate and up to date.
- AI-Driven Chatbots & Voice Assistants: Brands are integrating AI-powered voice assistants into their websites and apps to provide seamless, hands-free customer interactions.
Voice search optimization ensures that brands remain visible in an era where people increasingly rely on spoken queries instead of typed searches.

The rise of DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure): A New digital frontier
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) are reshaping digital ecosystems by enhancing data storage, connectivity, and security. This trend is particularly relevant for industries dealing with large-scale data and IoT applications.
- Decentralized Cloud Storage: Companies are moving away from traditional cloud services to blockchain-based storage solutions for increased security and cost efficiency.
- Distributed Computing Power: Businesses can harness decentralized computing networks to reduce costs and improve processing power for AI and data-intensive applications.
- Secure Digital Identity: DePIN enables individuals to control their personal data, reducing reliance on centralized platforms and enhancing privacy.
Brands that integrate DePIN solutions can offer greater reliability, efficiency, and decentralization, appealing to tech-savvy consumers.

AI and Blockchain convergence: The ultimate tech synergy
The convergence of AI and blockchain technology is driving innovation in branding. This powerful combination is revolutionizing everything from supply chain verification to customer engagement strategies.
- Trust & Security: Blockchain ensures data transparency and security, reducing fraud and counterfeit risks.
- Smart Contracts for Branding: Automated smart contracts are streamlining partnerships, influencer collaborations, and digital transactions.
- AI-Powered Data Analysis: AI can process vast amounts of blockchain data to identify trends, customer behaviors, and fraud detection patterns.
This synergy is opening up new possibilities for brands looking to harness cutting-edge technology to build trust and efficiency.

Conclusion: Future-Proofing Your Brand
The branding landscape of 2025 is defined by technological advancements, consumer empowerment, and ethical responsibility. Businesses that embrace AI, decentralization, immersive experiences, and sustainability will stay ahead of the competition.
To thrive in this evolving environment, brands must be agile, innovative, and customer-centric. Are you ready for the future of branding? Stay ahead by adapting to these trends and building a brand that resonates with the next generation of consumers.