UI/UX design in 2025 demands more than static mockups—it requires dynamic, collaborative, and user-driven processes. Whether you’re designing a mobile app, website, or immersive 3D experience, the right tools can dramatically impact your speed, creativity, and user outcomes.
This comprehensive guide from Viartisan showcases the most powerful and up-to-date UI/UX design tools every product team should know. From early-stage wireframes to developer handoff and usability testing, explore which platforms can elevate your design workflow.
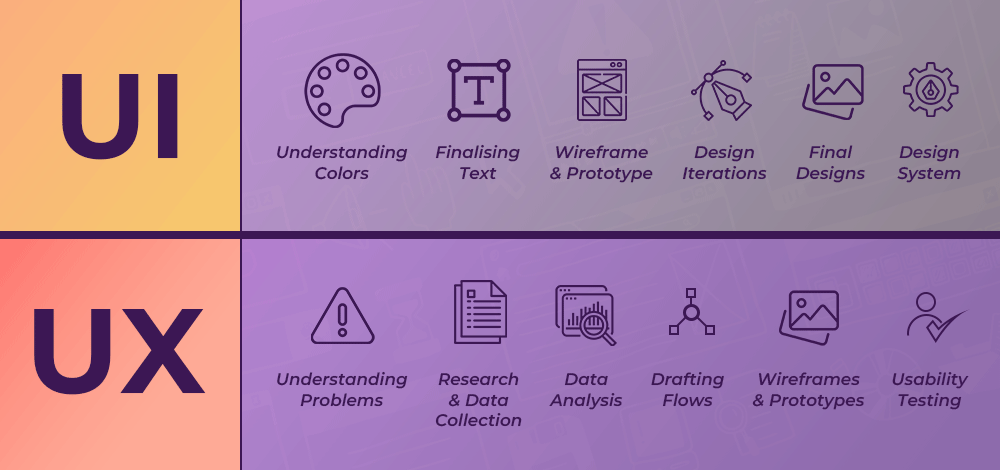
Why Choosing the Right UI/UX design tools Matters
The UI/UX workflow has grown more complex—spanning ideation, user research, wireframing, prototyping, testing, and collaboration. Choosing tools that match your design process means:
- Faster iteration & feedback loops
- Improved team communication
- Seamless developer handoff
- Better user-centered outcomes
Moreover, top tools today must integrate with agile workflows, remote collaboration, and cross-functional teams. Designers need tools that bridge creativity and engineering, empowering both rapid innovation and pixel-perfect implementation.

Top Categories of UI/UX design tools (2025 Edition)
1. Wireframing & Low-Fidelity Design
These tools help visualize structure, layout, and hierarchy before design polish:
- Balsamiq: Ideal for quick sketch-like wireframes
- Whimsical: Combines wireframes, flowcharts, and sticky notes
- Figma (Wireframe Kits): Fast, collaborative wireframing with real-time co-editing
Wireframes remain essential in clarifying navigation logic, page layouts, and information architecture before deeper visual design begins.
Tip: Use wireframes to align stakeholders before diving into visuals. A simple low-fi mockup can save hours of rework down the line.
2. High-Fidelity Design & UI Components
These platforms help designers craft beautiful, responsive interfaces:
- Figma: The industry’s #1 design platform for collaborative UI
- Adobe XD: Smooth Adobe integration and good for animation flows
- Sketch: Mac-only, plugin-rich environment for UI libraries
- Penpot: Open-source alternative with growing feature parity
Figma has cemented itself as the gold standard due to cloud-first architecture, design systems, and Dev Mode. Meanwhile, Sketch remains popular in Mac-based workflows, and Penpot is gaining attention in open-source communities.
Read: Why Figma Dominates the Design Stack in 2025
3. Prototyping & Animation Tools
Prototype real interactions without code:
- ProtoPie: Advanced interaction logic, sensor inputs
- Framer: Component-based design, ideal for product-led growth teams
- Principle: Timeline-based animations for mobile microinteractions
The gap between design and development shrinks when designers can build smart, animated prototypes that simulate true user flows.
Prototypes reduce dev misalignment and improve stakeholder buy-in. Pair with usability testing for even stronger results.
4. UX Research & User Testing Platforms
Validate assumptions, test usability, and analyze behavior:
- Maze: Remote usability testing with direct integration from Figma
- Useberry: Quick first-click and preference tests
- Lookback.io: Live moderated testing + video playback
- Hotjar / FullStory: Behavioral analytics via heatmaps and session replays
Research is no longer optional—tools like Maze and Lookback allow even small teams to gather data-driven insights pre-launch. Combine qualitative and quantitative testing for richer UX validation.
Insight: Use data from real users—not just internal reviews.
5. Design System & Handoff Tools
Ensure scalability and dev-ready designs:
- Zeplin: Handoff-ready specs, style guides, and asset exports
- Storybook: UI components with code and design documentation
- Figma Dev Mode: Code-inspection and dev handoff without leaving the file
- Zeroheight: Build design system documentation your whole team can use
With design systems at the core of modern design ops, these tools ensure cross-team consistency and scale. Storybook + Figma is a common combo for teams standardizing atomic UI systems.

Specialized UI/UX design tools for 2025
Accessibility Tools
Design inclusively with:
- Stark: Built-in accessibility checks inside Figma/Sketch
- axe DevTools: Automated WCAG compliance tests in-browser
- Color Oracle: Simulates colorblind views to test visual hierarchy
A11y is no longer a nice-to-have—it’s a business and legal imperative. These tools help embed accessibility early in the design process.
Collaboration & Feedback Tools
Remote and hybrid teams need powerful whiteboarding:
- FigJam: Figma’s whiteboarding tool for workshops, brainstorming
- Miro: Industry leader in remote design sprint facilitation
- Notion: Combine documentation, design process, and research libraries
Real-time collaboration has become a core UX discipline, not just a process add-on.
AI-Powered Design Tools
Boost ideation and automation:
- Uizard: Turn text prompts into wireframes instantly
- Relume: AI site map + component generator
- Framer AI: Auto-layout and real-time UI generation from copy
Generative design is here. Smart UI tools reduce friction, speed up exploration, and help non-designers prototype confidently.
Future-facing design means embracing AI + automation for scale.

How to Choose the Right UI/UX design tools stack
There’s no one-size-fits-all. Consider:
- Team size: Small teams may favor all-in-one tools (e.g., Figma)
- Design fidelity: Do you need wireframes, visuals, animation—or all three?
- Collaboration level: How async or real-time is your workflow?
- Developer involvement: Is handoff manual or deeply integrated?
- Project complexity: Does your app span mobile, web, or 3D environments?
Build your toolkit with modularity in mind—start lean, then layer on specialty tools.
Final Thoughts
The best UI/UX tools don’t just create beautiful designs—they enable faster thinking, clearer communication, and better product outcomes. In 2025, product success depends on cross-disciplinary collaboration, and your tools should be bridges—not bottlenecks.
Invest in tools that fit your team, your product, and your culture. And remember: tools evolve fast. Stay curious, test often, and keep your stack lean but powerful.
At Viartisan, we help startups and enterprises streamline design ops and scale intuitive user experiences. Whether you’re building a SaaS platform, mobile app, or 3D interface, we can help you choose, implement, and optimize the best UI/UX tools.
📩 Contact our team for a custom workflow or tool audit.